Oxalic acid (20 g)
Oxalic acid is a highly effective remedy for combating varroatosis of bees.
Application
To prepare a 2% solution of oxalic acid, the contents of the package are dissolved in 1 liter of warm boiled water. Treat the inter-frame space of the hives using a "Rosinka" type sprayer at a distance of 25-30 cm, at an angle of 30-400 to the frames, at the rate of 5-10 ml of solution for each inter-frame space.
Spraying is carried out three times in the spring, with an interval of 1 week, and in the fall, after collecting honey, at an air temperature not lower than +15 0C.
Application practice (research)
Studies have confirmed that the acid solution is most effective at concentrations of 1.4-2.7%. Various researchers have noted the high acaricidal activity of this drug, used in the form of a 2% aqueous solution by irrigating bees using an aerosol spray.
According to the literature, oxalic acid has no less acaricidal activity against the varroa mite than formic acid, and sometimes even more effective. And in some cases, it has a more gentle effect on the physiological state of bees than the formic one. The average effectiveness of treatments with oxalic acid solution is up to 90%.
This technology for using oxalic acid has a number of features. In particular, this is a strict temperature regime (the air temperature during treatments should not be lower than 16°C), labor intensity, the need to disassemble the nests and remove the frames one by one, which often leads to cooling of the nest and brood. During autumn treatments, the humidity in the nests increases, which contributes to molding of the honeycombs and the development of ascospherosis. In addition, mushrooms spoil beebread, and bees are poisoned during wintering.
When oxalic acid is stored in solution, it quickly loses its acaricidal properties.
In literary periodicals there is evidence that the method of treating bees with oxalic acid vapor was obtained while heating the drug in a special device. At the same time, good development of bee families and their high productivity were noted.
To study the effect of oxalic acid on varroatosis using the distillation method, studies were carried out under apiary conditions.
To do this, 25 families of bees were selected and treated in this way: 2 g of oxalic acid was poured into the working chamber of a special device (for every 10-12 frames), then the working chamber was heated for 30-40 seconds with a blowtorch, and the outlet tube of the device was inserted into hive entrance and, using a car pump, introduced acid vapor into the bee colony. After this, the hive entrances were closed for 5-10 minutes.
A control group of bee colonies was treated with a 2% aqueous solution of oxalic acid: the bees were irrigated, one by one removing frames with bees from the nest, using a “Rosinka” aerosol sprayer, the solution was applied to the frames with bees at an angle of 45 °C.
After the experiment, it was found that the efficiency of the oxalic acid distillation method is on average 93%, and the efficiency of the drug irrigation method is 79.5-80%.
Bipin and oxalic acid in the fight against varroatosis
In recent years, bee treatments have been effective during the broodless autumn-winter period, when the mite moves to the bees and attaches itself under the tergites, and therefore becomes inaccessible to the action of the drugs.
To excite the tick, a 20% alcohol tincture of mint is used (before treatment with bipin and oxalic acid, 10-15 minutes), under the influence of which the ticks become active, emerge from under the tergites and are vulnerable to the active substance of bipin and oxalic acid.
Before treating bees, the contents of the ampoule with bipin are dissolved in 2 liters of water (25-30 degrees C) and mixed thoroughly. You can use a plastic bottle with a hole 0.5-1 mm in diameter in the cork. Water the bees in the streets with a thin stream, passing the bottle from the beginning of the street to the end twice, at the rate of 5-10 ml of solution per street. If there is brood in the bee colony, the treatment must be repeated after 7-10 days.
Use oxalic acid in a 2% concentration (20 g per 1 liter of boiled water at a temperature of 25-30 degrees C). The solution is used by irrigating honeycombs with bees using “Rosinka” (5-6 pumps). Ticks fall off within 3 days.
The effectiveness and toxicity of bipin and oxalic acid were determined in the autumn, after feeding with sugar syrup, when there was no longer brood in the families.
Bipin began to act in the first 4-5 hours and caused massive shedding of ticks. Its action turned out to be somewhat more effective than oxalic acid. This was shown by comparative experiments.
Some beekeepers use various electric evaporators made from small glass containers, metal tubes of various diameters, or ordinary smokers. The essence of the techniques is to use electricity as a source of heating oxalic acid. Practitioners note that treating bees with oxalic acid vapor has a number of advantages over using a 2% solution of this drug, since it is carried out later in the fall or early spring, when there is no or little brood in the colonies. However, it should be noted that such heaters are available to beekeepers who have certain skills in working with electrical appliances. Such evaporators can only be used in electrified apiaries with the strictest observance of safety precautions - at least two people must work. One of the methods of application is the following: 20 g of oxalic acid is dissolved in 100 g of warm water, then 10 ml (per family) of the resulting solution is taken with a syringe and passed through a hollow copper bar heated strongly on a primus or gas stove. On one side, a medical needle is hermetically mounted into the blank with the cannula exiting outside. The vapors formed upon contact with the hot walls of the chamber are smoothly pumped into the hive through a tap hole through a fitting and a rubber hose. When checking the internal walls of the evaporator chamber, no deposits of acid crystals were found on it. Treatment against varroa by this method is carried out at any time of the active season in the evening. This method is still not recommended for practical use; it can be tested on a small number of bee colonies. You cannot use it during the honey harvest period.
Another way to use oxalic acid is by sublimation.
According to the instructions for the use of oxalic acid for varroatosis of bees, approved by the Main Directorate of Veterinary Medicine on November 21, 1988, it is used in two ways: by finely spraying bees with a 2% solution or with acid vapor obtained by sublimating it in a special device. To prepare a 2% solution of oxalic acid, use boiled water cooled to 30 °C (take 20 g of the drug per liter). The solution is prepared before use. In order to compact the bees on the frames, full-honey and beebread honeycombs are removed from the hive. Then the frames are removed from the nest one by one and the bees are sprayed on both sides with any fine spray (Rosinka, Bleskom, garden sprayer, etc.). The aerosol torch is directed directly at insects from a distance of 35-40 cm at an angle of 45 °, spending 10-12 ml of solution per frame (100-120 ml per family). Processing in multi-hull hives begins with the lower body.
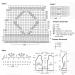
When treating bees with oxalic acid vapor in the hive, the upper entrance is closed, and 10-15 puffs of smoke from a smoker are introduced into the lower one. Then 2 g of the drug is poured into the working chamber of device 1 (calculated for every 10-12 frames occupied by bees) and the output tube 2 is heated with a blowtorch or other heater for 5-6 s, then it is introduced into the lower entrance and then 30- Warm up the working chamber for 40 s. After this, briefly, for one second, open valve 4 on the inlet tube 3 to supply oxygen or carbon dioxide from the cylinder under a pressure of 1.5 atm. In their absence, the acaricidal mixture can be supplied from the working chamber of the device using a car pump (4-5 full strokes). Before filling with a new dose of acid, the working chamber is cooled briefly (1-2 s), lowering the bottom onto the surface of cold water.
Packaging: 20 g package
Product supply unit: 1 package 20 g
Oxalic acid used to soften tap water for watering indoor plants at the following rates: 1/8 - 1/4 teaspoon per 5 liters of water. For 2-3 days after adding oxalic acid, the water should be in an open container to remove the chlorine vapor contained in it and precipitation of insoluble substances. After this, the water must be poured into another container, being careful not to disturb the sediment. Water the plants with this water.
Concentrate - 20 grams a.c. for 1 liter of water. For watering - 1 tsp. concentrate per 1 liter of water.
I use both methods. The first time I use 5-liter containers for drinking water.
Our water is very hard, as soon as I found out about this softening method, I immediately started using it.
This is the sediment after adding cabbage soup. acids.
And this is for comparison. In the left container, water with the addition of oxalic acid was used. On the right is filtered, settled ordinary tap water. There is a serious difference. 
I use a solution of sorrel. acids for about a year. I forgot what a coating on the surface of the soil is. The plants (besides violets, I have about 30 others) do not complain; Dieffenbachia even produced this:

Traces of limescale on your plumbing are the first sign that you have to use hard water. For most Russian regions, this problem is practically unsolvable. And you need to constantly make efforts to keep your bathroom or toilet clean. Otherwise, the bathtub, shower stall, faucets and toilet will become overgrown with limescale before our eyes, turning into something ugly.
Manufacturers of household chemicals make a lot of money by producing special products to combat limescale. Such products are usually not cheap, but the desired effect after their use does not always appear. But even if another gel does an excellent job of removing plaque, this does not mean that it is worth the money. You will probably be very surprised if you learn a simple thing: the active substances in many drugs are acetic, oxalic and citric acid - affordable and inexpensive products that can be bought for literally pennies. Therefore, reasonable and thrifty owners prefer half-forgotten home techniques to well-promoted brands.
How to deal with limescale using acids? And how do they act on certain surfaces?

Acetic acid
This does not mean table vinegar, but acetic acid or essence with a concentration of 25%. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:20. The denser the limestone formations, the higher the temperature of the water for preparing the solution. For example, it is recommended to clean faucets, shower heads and shower hoses with a metallized coating with vinegar, which has been previously diluted with boiling water (solution temperature - 100 degrees).
When working with acetic acid, you must be extremely careful and avoid getting it on your skin and, especially, your eyes. Be sure to wear thick rubber gloves.
Acetic acid can be used to remove traces of limescale from earthenware, nickel-plated, enameled, glass and metallized coatings. But an acrylic bathtub or plastic walls of a shower stall should not be cleaned in this way.

Oxalic acid
Also used in the form of an aqueous solution. It is recommended to dilute oxalic acid for cleaning the bathroom with warm water, and you should get a 5% solution. It is applied to surfaces made of glass, plastic, sanitary ware, and metal. You can also treat an enamel-coated steel or cast iron bathtub with oxalic acid solution. This is usually done with a brush. You need to wait 2-3 hours - during this time the oxalic acid will have time to “loose” the limescale deposits, and it can be easily washed off with a stream of water.
By the way, it is oxalic acid that is present in the well-known drug “Sanox”. But the problem is that the concentration there is too thick, and it is absolutely impossible to leave the applied composition on any surfaces for 2-3 hours. It is washed off literally immediately, since it dissolves limescale in a matter of seconds.

Lemon acid
The most delicate of all acids. It is safe for any coating, including acrylic bathtubs. To remove limescale from plumbing fixtures, regular “culinary” citric acid is suitable. Some even use natural juice from fresh lemons.
The method of application is as follows: a packet of citric acid is diluted with two glasses of warm water. A prerequisite: make sure that all the crystals are properly dissolved in the water, otherwise when cleaning they can scratch the surface of the vulnerable acrylic plumbing. Moisten a sponge with the prepared solution and treat everything that is covered with plaque. The process of neutralizing it will take from one to three hours, depending on how old and dense the layers turn out to be. After this time, the plumbing fixtures can be wiped again with a sponge soaked in the solution and rinsed with clean water.
What is oxalic acid
The element was first synthesized in 1824 by Friedrich Wöhler. Oxalic acid is an element, which among scientists is also called ethanedioic acid, belongs to the category of organic (dibasic) acids. In nature, the substance can be found in the form of potassium and calcium oxalates or in the free state. The substance has found wide application in everyday life, science, the food industry, and agriculture and is found in many products that people consume every day.
Oxalic acid formula
The discovery of this substance greatly influenced all organic chemistry and made it possible to make new discoveries. Salts of oxalic acid are called oxalates. They are divided into molecular, acidic, and medium. Most of them do not dissolve in water, but if you use pure acid, it mixes easily with it. Of the oxalates, only alkali metal and magnesium salts can interact with liquid. The structural formula of the substance is as follows: NOOCCOOH.
Preparation of oxalic acid
The extraction of this substance is usually necessary for industrial, domestic or scientific purposes. Oxalic acid is produced by the oxidation of sugar with nitric acid in the presence of a catalyst for the reaction of vanadium pentoxide. Below will also be a list of which foods contain oxalates; they are also found in all plants. The following obtaining methods are used:
1. Carrying out the oxidation of glycols, carbohydrates, alcohols using sulfuric acid in the presence of V2O5.
2. In the presence of Pd(No3)2 or PdCl2, oxidation of ethylene or nitric acid.
3. Sodium formate intermediate is prepared from carbon monoxide and sodium hydroxide. When heated, it produces sodium oxalate, which releases oxalic acid in an acidified state.
Properties of oxalic acid
The discovery of this element influenced many areas, from its use in everyday life to beekeeping. The salt of oxalic acid has both chemical and physical properties. Each of them can be used to achieve specific goals in the textile industry, chemical production, and food industry.
The following properties of the substance are distinguished:
Physical. It is a hygroscopic, crystalline, colorless substance. Can partially dissolve in ethanol (alcohol), water and is odorless.
Chemical. There is a peculiarity of dicarboxylic acids - they mutually influence each other, which facilitates the dissociation process. Oxalic acid is one of the strongest acids of this type, significantly superior in strength to its homologues.
Application of oxalic acid
The most popular uses of this substance are bleaching and cleaning. The use of oxalic acid helps remove rust, which is why most bleach/detergents contain this chemical. Widely used to soften and purify water, is included in cleaning products for sinks and toilets, and has a disinfecting effect. About 25% of the production is used as a dyeing agent in textile and leather industries. The acid can be used as a reagent for analytical chemistry.
Carboxylic acid is used for:
amenorrhea; infertility; bleeding; migraines; atypical menopause; helminthic infestations; sluggish bowel; chronic tuberculosis; sinusitis, sinusitis; impotence; intestinal infections; rheumatic pain; chlamydia, trichomoniasis.
We should not forget that excessive consumption can lead to disruption of the calcium absorption process. For this reason, oxalate stones can form inside the genitourinary system. Harmful formations pass through the urinary ducts, turning black due to blood, injuring the mucous membrane. This leads to acute pain in the back, groin, abdominal cavity, and changes in the color of urine.
An overdose of the substance can cause: dizziness; weakness; pain in the stomach; stomach upset; burning of the throat, mouth, sinuses; nausea.
What products contain
There are two options for obtaining the element - synthetic and through the destruction of wood. There are also products containing oxalic acid, which many people use daily in their menu. The percentage of the element is relatively low, so an overdose is extremely unlikely and it does not pose a danger. The content varies, below is a list of which foods contain more than 10 mg of acid per 0.5 cup.
rhubarb; zucchini; spinach; carambola; beet tops; strong tea; gooseberry; spinach; draft beer; beans; salad; orange, lime, lemon; instant coffee; sorrel; figs; chicory; leek; strawberry; tomatoes; butter dough; Red Ribes; wheat bran; green vegetables; parsley.
Dilute 10 ml per 10 liters of water.
You can spray and water the plants.
The solution can be used continuously or periodically to water all plants. The solution does not deteriorate and can be stored for a very long time.
Plant growth stimulants are currently becoming increasingly popular. There are a huge variety of them on the market for gardening products. However, many very, very effective stimulants can be purchased much cheaper than what is offered in colorful packaging. One such stimulant is oxalic acid. Many organic acids exhibit a stimulating effect on plants. For example, they stimulate plant growth and increase their resistance to drought and other unfavorable conditions
vinegar, amber,
maleic, fumaric,
citric, formic acid...
We have already talked about the advantages of some of them and recommended using them in different ways. It is very important to use them correctly, because if used incorrectly, instead of stimulation, you can get depression (after all, it is well known that hypervitaminosis is no less dangerous than vitamin deficiency, and this is also true for plants). And many recommendations are still to come. Today it’s the turn of oxalic acid.
Oxalic acid and its salts in high concentrations are toxic! Therefore, when working with it, as with other means. used in agriculture, you must be careful! To eliminate the risk of accidentally drinking a solution of oxalic acid, drop some brilliant green, blue, solvent, gasoline, etc. into it. - to make it clearly distinguishable from water and unpleasant to drink. For gardening and vegetable gardens, oxalic acid is simply an irreplaceable tool: its solutions are used
for soaking seeds,
foliar treatment of plants,
spraying or watering throughout the growing season.
This allows
increase plant resistance to unfavorable environmental factors,
improve decorative properties,
slow down the aging process of plants,
suppress the development of harmful and undesirable organisms in the soil and on the plant,
reduce the decline of flowers and ovaries of vegetable plants.
When soaking seeds, spraying and watering plants, oxalic acid is used in very low concentrations. In this regard, it is advisable to first prepare a stock solution, which is subsequently diluted to the desired concentration.
Since oxalic acid works better in the form of ammonium oxalate salt, it is advisable to add ammonia to the acid solution.
1 tsp. oxalic acid,
diluted in 0.5 liters of water
with the addition of 2 tsp. 25% solution or 5 tsp. 10% solution,
enough for 500 (!) l. ready solution,
which can be used to spray and water plants. This solution can be used constantly or periodically to water all plants.
Cucumber is very responsive to it.
If the varieties of cucumber we are usually accustomed to bear fruit within several months, then in a greenhouse it is possible to extend fruiting to a year and a half!!
Soil watered with water containing oxalic acid is free of pests such as
like nematodes, wireworms, chafer larvae.
Another plus: when watering plants with such a solution, the calcium and magnesium carbonates and bicarbonates contained in the soil are gradually replaced by calcium and magnesium oxalates, which serve as a source of these elements in the soil, while at the same time they do not have a harmful effect on plant roots like carbonates and bicarbonates in high concentration (this is especially important on alkaline or chalky soils, chernozems). Calcium and magnesium in the form of oxalates are not subject to leaching from the soil, as happens with carbonates (and this is very important for more acidic soils, in which the risk of blossom end rot of tomato, zucchini and other plants is high).
This simulator is cheap, economical, easy to use and in ultra-small dilutions is non-toxic for humans and plants, it acts very comprehensively - both as a stimulant, and as a means of getting rid of soil pests, and as a fixator of useful elements in the soil, and as a means of extending fruiting periods. plants.
Oxalic acid, unfortunately, is not sold in every store or pharmacy. Although it is often included in anti-scale products. Read the ingredients, and if it is there, you can safely use these products. Other components, being very strongly diluted in water, will not have a negative effect. In addition, oxalic acid is sold in stores and on websites for beekeepers.
But those who make herbal fermentation (green fertilizer) can systematically add different types of sorrel and other plants containing high concentrations of oxalic acid (quinoa, beet tops, including sugar and fodder, and in many other plants, including weeds) to enrich the fertilizer with oxalic acid. And who knows - maybe the value of this fertilizer is not so much in nitrogen, but rather in oxalic acid?