Greetings, dear friends!
If you want to grow gourds, a beginner melon grower should first deal with the capital cultivation and fertility of the site planned for the cultivation of melons and watermelons. Balancing soil nutrition in the agrotechnology of the pumpkin family is the main component of productivity, sugar content and quality of grown fruits.
The use of fertilizers in the cultivation of gourds
With fertilizers for melons, pumpkins and watermelons, accuracy and literacy are necessary, since these crops are poorly adapted to the synthesis of useful trace elements and, like a sponge, accumulate heavy compounds and nitrates in their fruits. Therefore, all types of dressings during the growing season should have an easily digestible form in the form of humic, ash and green concentrates, and active organics with granular minerals should be introduced in advance during the autumn digging of the site. If you use manure or minerals in their natural form, feeding gourds during the growing period, for example, watermelon, its fruits will be supersaturated with nitrates, with tasteless pulp, speckled with white inedible veins, with a triple thickened rind and unripe seeds.
Irrigation technology for growing gourds
With active watering, you can increase the yield of melons by two to three times. The most important period of water flow to the roots is the time from the appearance of the first shoots in the garden to the start of fruiting. During this period, the root system of gourds is still not strong enough to provide the necessary amount of moisture, especially for melons. For the whole season on melons, it is necessary to produce at least three plentiful waterings. The first irrigation is necessary during the appearance of the first shoots and the formation of dense foliage. The second watering is important during the period of active flowering of plants. The third time it is necessary to shed the plantings at the very beginning of the formation of fruit ovaries, after which the irrigation of melons is completed. If you continue the "water procedures", they will already be harmful - the likelihood of cracking of ripened fruits, low sugar content, deterioration in taste, and a decrease in the shelf life of the crop increase. After the final third irrigation, a good humic top dressing will not damage the plantings.
Care of gourds
Conducting cultivation of gourds, during the summer, the shoots of plants are necessarily pruned, since with unregulated growth of tops, the productivity and quality of the crop deteriorate. After waiting for the appearance of 5-6 leaves on the shoot, you need to cut it over the second leaf. At the cut site, a pair of shoots is subsequently formed, which also need to be pinched, and when 8-9 leaves appear, the shoot is shortened to the sixth leaf.
When ovaries appear, the upper part of the petiole is cut so that a couple of sheets remain on top. As soon as melon ovaries become visually comparable in size to an apple, the least strong of them are cut off. The remaining lashes with ovaries should be placed on the ridge so as not to interfere with their growth: provide access to sunlight and avoid growing beyond the borders of plantings. It is undesirable to leave infertile lashes, it is better to cut them out completely so that they do not take on themselves the nutrition, water, light necessary for the ovaries and do not interfere with the ventilation of the fruit-bearing, green mass.
I wish you to harvest a good harvest of gourds. See you!
The homeland of gourds is tropical and subtropical latitudes, so they need light sandy lands. Bakhcha cannot consist of chernozem. But climatic conditions do not matter much. Fruits from the Pumpkin family grow well both in the south and in the Far East. The exception is the regions of the Far North. Difficulties in obtaining a crop will arise when planting watermelon and melon, but for these plants there are technologies for growing in greenhouses.
Characteristics of melon varieties
The list of plants growing on melons includes watermelons, melons, zucchini, squash, pumpkins. Most of them have long creepers creeping along the ridges with large leaves and yellow single flowers. They tolerate dry weather well, as their powerful and strong root system can "extract" moisture from the deepest layers of the soil.
Melon growing is a simple science. Cultures require a lot of sun and heat, the weather at the time of growth should be hot and dry. But when purchasing seed material, it is important to pay attention to the duration of the growing season. If the landing area involves a rapid summer, only early species are planted with a ripening cycle of no more than 90 days.
Watermelon
There is a huge variety of varieties of melons such as watermelon. In addition to the fact that there is a division into table and fodder species, this berry is different in weight, shape, color of the pulp and peel, taste, place and method of cultivation.
General characteristics of the plant:
- 1. Stem resembling a creeper - long, flexible, curly, rounded, can reach 5 m in length.
- 2. The leaves are wide, attached to the trunk with short petioles. The leaf plates are large - about 25 cm long, 20 cm wide.
- 3. The flowers are yellow - 2.5 cm in diameter, unisexual.
- 4. Fruits are oval, round, square, pyramidal.
- 5. Pulp with numerous seeds - yellow, red, pink.
To date, more than 1000 varieties of the largest berry in the world have been grown, and all of them are not alike. Unusual can be not only the form, but also the content. Recently bred seedless fruits are surprising. They are grown using a special pollination technology.
The following groups of watermelons are conditionally distinguished:
No. p / p | Description | A photo |
|
Colocynth | The plant has round leaves, large flowers, small fruits. The peel of a ripe watermelon is yellow, dense. The flesh is white with a slight yellowish tint. It has many useful substances. In some countries it is used as a remedy. Suitable for the preparation of powders, extracts, oil is squeezed out of seeds |  |
|
Ordinary | The largest species group of watermelons, annual. The shape is ellipsoid or round, the peel is green to dark green in color with or without stripes. The flesh is red, white, yellow. It has a high sugar content, the size depends on the place of cultivation. The seeds are dark, flat, the stems are like a creeping liana, the leaves are fleecy, hard about 22 cm. Excellent taste |  |
|
Square | Similar to ordinary. The unusual shape facilitates easy transportation and storage. The cubic configuration is obtained due to the peculiarities of growing: when the future watermelon reaches the size of a large onion, it is covered with a cube of plywood or wood |  |
In areas with a cold climate, seeds are not planted directly into the soil to increase the ripening period. The first step in growing watermelons is planting seedlings in early spring. Only in this case, a fully matured product is obtained by mid-September.
Melon
The fragrant fruit belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family. The pulp contains a large indicator of easily digestible sugars, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and more. Recommended for use in case of deteriorating health:
Unlike watermelon, which is considered a berry, melon is recognized as a vegetable.

Melon is an excellent adjuvant for many diseases, it is recommended by doctors as a nutritional component. But still, this fragrant fruit has contraindications:
- 1. Not recommended for diabetics, as the product contains up to 13-15% sugars (depending on the variety). If the patient has a disease of the 2nd degree, you can use a bitter variety, it reduces the glucose index.
- 2. With liver diseases.
- 3. Children under one year old.
- 4. With great care for those who have gastritis and ulcers.
- 5. Diarrhea and other gastrointestinal disorders.
- 6. In diseases of the spleen, the fruits are consumed with honey.
Melon is 90% water, in addition it contains a huge amount of carbohydrates. Therefore, nutritionists recommend using it as an independent dish, without mixing with other products.
Pumpkin
The shape of the fruit can be very diverse - round, oval, small (decorative) or large, have a hard crust on top and pulp inside. All these parameters depend on the variety and growing conditions. Flat seeds about 3 cm have nutritional and medicinal value.
Pumpkin is a very important agricultural plant, it is easy to grow, and subsequently there are no difficulties with storage. In cooking, the vegetable is used to make mashed potatoes, soups, for sweet pastries, jam, juice, etc.
Vegetables are used for the following diseases:
- anemia and other types of anemia;
- male weakness;
- cardiovascular disorders;
- diseases of the nervous system;
- various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- obesity
- chronic tuberculosis, etc.
However, there are a number of contraindications and limitations:
- 1. Not used for diabetes of all degrees.
- 2. Raw fruits and juice are prohibited in ulcers.
- 3. Juice in its pure form is not drunk in case of violations of the digestive tract.
The body of some people does not tolerate any variety of pumpkin, an allergic reaction is possible.
Zucchini and patisson
The list of gourds additionally includes squash and zucchini. They are similar in taste, the presence of nutrients and minerals, beneficial properties for the body and contraindications.
The benefits of vegetables:
- 1. Squash skin contains antioxidants that rid the body of free radicals, prevent the development of oncology, and preserve youth.
- 2. They contain potassium, which is necessary for the heart muscle and normalization of pressure.
- 3. Both vegetables contain fiber, which reduces the risk of neoplasms in the rectum.
- 4. Squash serves as a natural source of the substance folate. It is important in cell division and DNA synthesis.
- 5. Controls the level of bile and glycogen.
- 6. Due to the diuretic property, excess fluid and sodium salts are removed, causing its retention.
- 7. Squash is useful as an adjuvant in prostate cancer.
Medicine claims that both zucchini and squash contain a fairly large amount of vitamins (C and group B). But it must be remembered that the data presented in various sources correspond to fresh vegetables.
Harmful properties of zucchini and squash:
- 1. Canned gourd derivatives are not recommended for use by those with diabetes.
- 2. Not indicated for hypotensive patients.
- 3. Should not be used for digestive disorders and gastrointestinal problems.

Growing crops of the Cucurbitaceae family
There are cardinal differences in planting and growing vegetables depending on the region. If in the south it is enough to plant seeds in the soil, perform minimal care manipulations and harvest after a while, then in the central part of the country and the Far East it is necessary to carry out preliminary work both before planting and for growing melons.
Experienced melon growers advise sowing seeds for seedlings as early as March. Until the summer, she is kept in the apartment on the windowsill. And only at the end of May - the beginning of June they are planted on a prepared garden bed. Transplantation is carried out extremely carefully, since the root system of gourds is very fragile and delicate. A method of transshipment of an earthen coma is suitable.

The nuances of melon growing in cold regions
And watermelons, and melons, and zucchini are grown almost everywhere. In order for this to be possible, experts advise:
- 1. In the middle zone of the country, plant melons in the ground, but at the same time cover each sprout with a plastic bottle cut in half. The lid should be removed before watering. On top of the 1.5-liter bottle, place a 5-liter container, cutting off the bottom. When the plant outgrows a small container, it should be removed, leaving a large one. This will turn out a mini-greenhouse for each sprout.
- 2. In order for the vegetable to be filled with sunlight, the melon should be arranged in an open space without shaded areas. But with strong sunshine, the plants should be covered for a short time with large leaves of burdock or use a light awning.
- 3. For ease of care and space saving, it is better to start the vine on supports. Along the beds with plantings, you need to stick the poles, pull the wire in 2-4 rows on them, and let the stem run along this support.
- 4. During prolonged rains, the fruits lying on the ground will begin to rot, so under them it is necessary to put small boards, polystyrene, build sand mounds, create some other safety cushion.
- 5. In the central and eastern regions, very often groundwater occurs close to the surface. Therefore, the overgrown roots, having reached them, begin to rot. If you initially water the plant not under the bush, but a little far away, the root system will not go deep, but will grow to the sides.
- 6. On melons, whips that have arisen are subject to mandatory pruning. Leave one large stem-liana with flowers.
- 7. Pinching is carried out after 6 flowers. If you leave more, the fruits will be small and tasteless.
All care for gourds after planting seeds or seedlings in open ground consists in abundant watering, pinching, fertilizing, protection from decay and protection from diseases.
Disease Control Measures
The first step in the fight against diseases of gourds is the disinfection of seeds before planting. Etching is carried out using a solution of copper sulphate or zinc sulfate.
Other measures are presented in the table:
Disease | signs | The reasons | Treatment |
Fusarium | The fungus penetrates the root system and cannot be visually detected in the first stages. | Waterlogging and night temperature drop to +16° | The plant should be removed, the soil should be disinfected with copper sulphate |
Anthracnose | Yellow and brown spots appear on the leaves, then they increase, spread, forming ulcers, the fruits rot | The causative agent is a fungus that is originally in the ground | Spot spraying with Bordeaux liquid. The course consists of 3 procedures with an interval of a week. The soil is disinfected with potassium permanganate or copper sulfate |
root rot | Weeping brown and black spots begin to spread from the bottom of the leaf, move to the shoots, eventually absorb the entire plant | Extremely variable temperatures and humidity, excessive root fertilization | They are treated only at the first stage: the water for irrigation is replaced with a solution of potassium permanganate, the roots are taken out of the ground, treated first with copper sulphate, then sprinkled with ash, and after treating the soil, they are buried. In advanced versions, gourds are destroyed |
Bacterial spotting | The fruits develop spots that are watery to the touch and yellow-green in color. Over time, they grow, turn into growths, the leaf turns black, the fruit dies | The disease is carried by insects | There are no drugs for treatment. In the primary stage, all sheets are cut. If it does not help, the plant must be destroyed. |
powdery mildew | The leaves look like they are sprinkled with flour. Over time, the fungus turns brown, turns into a growth | The disease is fungal, found in the ground or on seeds | Bushes are treated with Karatan, Byleton, Topaz, the infected parts are cut and burned |
mosaic disease | Extensive light areas appear on the leaves, later the plant is deformed and dies | Viral disease transmitted by insects, contaminated tools and seeds | With primary signs, 2 times sprayed with Karbafos with a difference of 7 days |
leaf rust | The plant is sprinkled with shapeless tubercles of a rusty color. From the cracked tubercles, spores are poured out in the form of a powder | Infection with rust fungi as a result of an excess of nitrogen and high humidity | The affected parts of the plant are cut and destroyed, then everything is treated with fungicides. |
olive blotch | Weeping spots of a gray-green hue appear on the fruits, the leaves become brittle, the culture dies in 10 days | Unremoved infection in the ground | At the first stage, Bordeaux liquid is used. If time is lost, they are treated with Abigo-Peak, Oxyhom. Course 3 times, interval 7 days |
Growing any variety of gourds in Russia is not very difficult. It is enough to follow the elementary rules and carry out the prevention of diseases in time.

Lecture plan
a) the choice of soil and relief, the predecessor;
b) basic and pre-sowing soil preparation;
c) preparation of seeds for sowing;
d) timing of sowing seeds;
e) plant care and harvesting.
1. The choice of soil and relief, the predecessor.
Gourds do better on light sandy and sandy loamy soils, they grow worse on chernozems and chestnut soils. Poorly structured heavy loams are especially unsuitable for them.
An important role in the life of gourds is played by the relief of the site. According to the orientation of the site to the cardinal points, the slopes that are better illuminated and warmed up are most suitable - usually they are southern and southwestern. However, it should be noted that in very dry conditions, the southern slopes dry out faster and, due to the lack of soil moisture, are unsuitable for melon crops. Usually, crop rotations with gourds are located mainly on flat steppe spaces.
Melons are placed in field or fodder crop rotations. To obtain high yields, these crops are grown on a layer of perennial grasses or on virgin soil. Virgin and fallow lands are reserved for melons, most often on sandy soils. In non-grass field rotations, fallow winter wheat or row crops such as maize are a good predecessor. Of the main vegetable crops and potatoes, potatoes will be the best predecessor for melons; vegetable crops such as onions, cabbage and carrots are also good predecessors.
Undesirable is the permanent culture of gourds for several years in one place or their frequent return to the same field where they have already been grown. This contributes to the development of diseases and, as a rule, leads to a sharp decrease in yield. This is evidenced, for example, by the experience carried out at the Uzbek vegetable and melon station. So, if in the first year of melon cultivation in one area the yield was 164.6 centners per hectare, then in the third year it decreased to 71 centners per hectare. Also undesirable are compacted crops of gourds with corn, sorghum, as well as the placement of gourds in the aisles of orchards and vineyards. Which significantly delays the ripening of fruits, reduces the yield. The gourds themselves are good predecessors for other crops.
2. Basic and pre-sowing soil preparation.
One of the main conditions for obtaining high yields is the use of the correct tillage system. In the conditions of the arid climate of the south of Ukraine, the tillage system should include: an increase in the loose arable layer for the accumulation and preservation of moisture, the creation of favorable conditions for the water, air and food regime of the soil for the growth and vital activity of the root system. In addition, proper tillage is a means of controlling weeds and diseases. During autumn tillage, the timing and quality of autumn plowing are of particular importance. The timing of autumn plowing depends on the time of harvesting the previous crops, the state of humidity and the degree of contamination of the field. Long-term experiments show that the earlier autumn plowing is carried out, the greater its effectiveness. With early autumn plowing, more nutrients and moisture accumulate in the soil.
In areas freed from under early crops, plowing of fallow land for gourds and gourds begins with soil peeling immediately after harvesting the previous crops. Plant residues are destroyed by preliminary peeling, the topsoil is loosened, which sharply reduces the evaporation of moisture from the soil, and when there is little precipitation, it contributes to the rapid germination of weed seeds. Depending on the germination of weeds, 2-3 weeks after peeling, autumn plowing is carried out with a plow with a skimmer. If the previous crop is harvested late, then the plowing of the fallow is carried out without preliminary peeling, immediately after harvesting.
The main plowing is carried out, as a rule, in autumn, but on sandy soils, to prevent blowing out, the soil is plowed in the spring. The depth of plowing should be at least 25 - 30 cm, plantation and semi-plantage plowing is even better.
A large increase in the yield of gourds during deep plowing can be achieved by increasing the volume of the loose soil layer, which improves its aeration and food regime, increases the amount of water-soluble phosphoric acid, nitrates and moisture reserves in its deeper horizons. At the same time, a powerful root system develops, which penetrates much deeper into the soil than with conventional plowing. In addition, at deeper plowing, melons and gourds develop, as a rule, a two-tier root system, and not a single-tier one, as in conventional plowing.
Organic and mineral fertilizers are applied under plowing under gourds. In the steppe zone of Ukraine, on chernozems, rotted manure is used at a dose of 10 t/ha. The application rate on chestnut soils in the central part of the southern zone and in the Crimea is recommended to be increased to 15 t/ha, and on alkaline soils - up to 20 t/ha.
Following the autumn plowing, the site is planned in two tracks.
In the southern arid zone, autumn harrowing and fallow cultivation are becoming more common, which give particularly good results in years with insufficient soil moisture from autumn and during dry winters.
In early spring, at the first opportunity to leave the field, harrowing is mandatory. As a rule, this work is done quickly, in one to three days, and first of all, elevated areas are harrowed, where the soil dries out faster. Particular attention should be paid to fields with alkaline soils, since a delay in harrowing on such soils even for one day leads to the formation of a crust that is difficult to work.
Used in all zones of Ukraine, harrowing is accompanied by single and double cultivation, depending on the conditions of spring. The depth of cultivation should be such that no lumps remain on the surface of the soil after it has been carried out. Pre-sowing cultivation is carried out to the depth of seed placement. It is necessary to do it in such a way that immediately after it is carried out, the seeds are sown.
3. Seed preparation for sowing
Sowing melons and gourds must be done with seeds of promising varieties and hybrids that are conditioned in terms of germination. For sowing, it is better to use well-sorted large full-weight seeds (class I seeds). Large, healthy seeds contain more nutrients for the embryo and therefore produce more complete plants and higher yields. Seeds are sorted by specific gravity by immersing them in a 3% sodium chloride solution. Seeds can also be sorted by size, passing them through a sieve with cells of 1.5 × 1.5 cm. However, various centrifugal sorting machines are more productive, the SP-0.5 pneumatic sorting table is especially convenient for these purposes.
In order to combat fungal diseases, melon and pumpkin seeds are pickled. Many melon growers prefer two-four-year-old seeds, and when using one-year-old seeds, they heat them at a temperature of 35-40 ° C for five hours. This ensures a more uniform emergence of seedlings, accelerates the appearance of female flowers, fruit ripening and increases the yield. So in this case, the increase in the yield of gourds from heating can be 30 - 40%.
To accelerate the emergence of seedlings, melon seeds are soaked. Soak the seeds in a wooden, glass or metal stainless dish, pouring them with a layer of 15 cm. You can also soak the seeds in bags. In this case, the seeds should occupy no more than half the bag. Soak the seeds in water with a temperature of 18 - 22 ° C for 20 hours, changing the water after 10 hours. Seeds soaked in this way begin to grow faster.
Good results are obtained by the method of pre-sowing seed preparation proposed by P. Genkel. Seeds are alternately soaked for 48 hours at a temperature of 18 and 30 ° C and dried. This increases the energy of germination and germination of seeds, increases the intensity of respiration, activates the activity of enzymes and increases the yield.
Germination is an effective method of presowing preparation of gourd seeds, which significantly accelerates the emergence of their seedlings. Seeds are germinated so that they start growing, or, as they say, peck. Seeds are germinated in a bowl, on burlap or boiled sawdust with a layer of no more than 5 - 6 cm. Germination is carried out at a temperature of 25 - 30 ° C for 70 - 100 hours, while every 8 - 10 hours the seeds must be mixed. When slightly noticeable seedlings appear in 1/3 of the seeds, they are slightly dried and sown. Germinated seeds should only be sown in moist soil. If such seeds fall into dry soil, the seedling will dry out and die. From germinated seeds in moist soil, seedlings appear already on the 3rd - 4th day.
4. Terms of sowing seeds.
The timing of sowing will depend on local soil and climatic conditions and crops. Usually, the sowing of watermelon and melon begins when the soil temperature at a depth of 10 cm reaches 12 - 13 ° C. In the south of Crimea, this happens on April 5 - 15, and in the steppe regions on April 20 - 28, and on the Kerch Peninsula - in mid-April. Some melon growers prefer to sow in warmer soil - in the first days of May. Pumpkin is sown 8-10 days earlier than watermelon and melon.
The correct choice of the sowing time is a very responsible matter, since the friendliness of the emergence of seedlings and the size of the crop largely depend on it. With very early sowing in unheated soil, the seeds will swell, but they will not germinate and may die; if sowing is delayed, the soil may dry out and seedlings may also not appear. Usually, dry seeds are sown earlier, and wet and pecked seeds are sown later, but in such a way that the soil has sufficient moisture reserves.
In addition to the correct choice of the optimal sowing time, the size of the crop is affected by the feeding area. The feeding area of melons and pumpkins depends on the nature of the soil, the amount of precipitation and the length of the variety. For melons, the feeding area is 1 - 2 m2. A smaller feeding area is given on rich chernozem soils, a larger one is allotted on dry and sandy soils. Sow the seeds of melon and pumpkin in three ways: square-nested, row and tape. Square-nesting method, leaving two plants in the nest, late varieties of melon according to the scheme 140 × 140 cm.
In the ordinary way, early ripening melon varieties are sown according to the scheme 140 × 70 cm, pumpkins according to the scheme 280 × 70 and 280 × 140 cm.
More promising are the belt crops of gourds, as they allow to lengthen the period of mechanized processing of row spacing. Melon is also sown with a two-line tape according to the scheme (140 + 70) × 70 cm.
Sowing is carried out with seeders, which can be used to pick up interchangeable discs of sowing machines for each variety. These planters provide the right area of nutrition and good seed placement.
However, in the spring in the southern regions of Ukraine, the weather is dry and windy, the top layer of the soil dries up very much, and therefore it is difficult to get seedlings on rain-fed lands. Previously, with the manual method of sowing, water was poured into the wells. This is a very labor intensive job. Less time-consuming is mechanized sowing with adding water from tanks suspended on a tractor and connected by hoses to the seeder coulters. Such a unit is designed on the basis of the SKGN-6A seeder, sowing in a similar way allows you to get normal seedlings.
The seeding rate varies depending on the sowing scheme and seed size, and is 3-4 kg for watermelon, 2-3 kg for melon and 3-4 kg/ha for pumpkin.
Seeding depth depends on crop, sowing time, seed size and soil conditions. On heavy clay soils, melon seeds are sown to a depth of 3–4 cm, watermelons to 4–5 cm, pumpkins to 7–8 cm; on light sandy loamy soils, the sowing depth increases by 1–2 cm, respectively.
The sowing depth can be much greater: for melons and watermelons up to 8 cm, for pumpkins up to 10 cm.
After sowing, the soil is rolled with ringed rollers. This allows you to create better seed-to-soil contact and get more, better seedlings.
5. Plant care and harvesting.
Caring for melons and gourds consists in the timely breakthrough of plants, loosening the soil and the destruction of weeds, in the fight against diseases and pests. Timely, correct and thorough care of melon plants is a decisive target for obtaining a good harvest, since due to the loosening of the soil and the destruction of weeds, moisture and nutrients are retained in the soil.
Care for gourds begins with cultivation and the so-called row-spacing, which is often carried out before full shoots appear.
On crops of gourds, on some, transverse cultivation is used. Bouquets are left with sizes of 35 - 50 cm, and the gaps between bouquets are equal to the future accepted distance between plants in a row.
The first inter-row cultivation of crops personally begins at the time when the first true leaf develops in the plants. Since the root system of gourds at that time mainly develops in depth, it is better to process the row spacing to a depth of 14-16 cm to destroy weeds.
The second cultivation of melons and gourds begins in the phase of formation of 4 - 5 true leaves to a depth of 10 - 12 cm. The first two cultivations must be completed within 30 days after emergence.
The third and fourth cultivation is carried out as weeds appear and soil compaction, but no later than 12-16 days after one another. In order not to damage the root system of plants, the depth of cultivation should be no more than 8-10 cm, and in wet years deeper cultivation is acceptable, and in dry years the depth can be reduced.
If during the 3rd and especially the 4th cultivation there are large lashes, then they should, if possible, be moved to the nests, and after the passage of the machines, they should be laid out again in the aisles.
Simultaneously with cultivation on melon crops, manual loosening of the soil in nests or rows is carried out. During the period of these works, it is necessary to carry out thinning of plants. Shoots of gourds are thinned out twice: the first time when 2-3 true leaves are formed on plants, leaving 2-3 plants in the nest, or one in a row after 15-20 cm; the second end of thinning, leaving one of the most developed plants in the nest, is done in the phase of 3-4 true leaves. This period usually occurs 25 to 30 days after germination. Plants removed during thinning must be pinched off, and not kept, as in this case the root system of the remaining plants is disturbed. It is very important to thin out plants in a timely manner and preserve nutrients, the amount of their growth. Delay in thinning even by 5 - 7 days leads to a different decrease in yield (often up to 20% or less).
Recently, efficiency has been proven in some top dressings of melons. For foliar top dressing, various microelements are used. The most effective are boron and manganese. So, according to Karpov, it is sprayed with a three percent solution of boric acid in a proportion of 0.5%. And a solution of manganese sulfate at a concentration of 0.1% at the beginning of flowering and at the beginning of fruit formation increased the yield of watermelons by 30 - 34%. For foliar top dressing, various sprays are used.
Among the still little-studied methods that help increase yields, accelerate fruit ripening and improve the quality of gourds, the pinching of these plants deserves attention. In early ripe varieties of watermelon, melon, pinching must be done twice. The first time the plants will have 4 - 6 true leaves. The second time the plants are pinched during the formation of the link, and at this time the growth points should be removed from a larger number of developed stems, both fruit-bearing and non-fruit-bearing. If the weather is hot, then the removal of growth points from the stems must be done by the second half of the day, so that the plants can more easily endure this operation. Pinching is very important in areas with a short growing season, for example, in the middle lane, and when moving to more northern regions of the country.
Of the other methods of agricultural technology, the artificial pollination of melons deserves attention. As you know, in the southern regions of Ukraine during the beginning and mass flowering of gourds, there is a prolonged high air temperature, as well as drying winds. High temperatures and drying winds affect the process of normal pollination of delicate flowers, since in these far from optimal conditions, pollen quickly loses its ability to fertilize. If fertilization does occur, it is often insufficiently complete. In such cases, the fruits of the gourds turn out to be somewhat ugly in shape, and for the most part, having begun to develop, fall off. In these adverse weather conditions, artificial pollination of female flowers becomes important. According to Makarovsky, additional artificial pollination of watermelon and melon flowers, carried out 5-6 times in 3-5 days, increases the yield of watermelon fruits by 90%, and melons - by 200%. At the same time, the number of large fruits on additionally pollinated crops increased by 1.3 times in watermelon compared to unpollinated crops, and by 5 times in tribute. Makarovsky believes that due to additional pollination, about 50% of the ovary does not fall off.
In Zelenova's experiments, additional pollination of pumpkins increased the fruit yield by 40–150%, depending on the variety. Artificial pollination of gourds should be carried out only in the morning from 6 to 10 o'clock.
For a more complete natural pollination of gourds, beehives with bees are taken to the plantations for 10-15 days at the rate of one hive per hectare of melons. In order to improve the commercial qualities of fruits, it is possible to apply a rare, but very effective method of fruit formation, developed by melon growers. It consists in the fact that the fruits are set with the stalks up with the size of the ovary about the size of an egg. At the same time, all sides of the fruit develop evenly, its long diameter is slightly reduced, the fruits acquire the correct presentation and the quality of their pulp improves.
Table watermelons and melons are harvested selectively as they ripen, zucchini and squash are harvested when the fruits reach a standard size, pumpkins are harvested in the fall, when the crop mass ripens or before the end of the growing season.
The fruits of early-ripening varieties of watermelon and melon are harvested more often, and mid-ripening and late-ripening varieties are harvested more rarely. Depending on the variety and purpose, watermelon fruits are usually harvested 3-4 times, and melons - every 4-7 days. All varieties of pumpkin, as a rule, are harvested in one go after the green mass of the plants ceases to grow. It is better to harvest zucchini at the time when they reach 10 - 12 days of age, as this increases the productivity of plants. Periodic collections of ripe fruits from watermelons, melons and pumpkins also contribute to better development and the formation of new fruits.
During maturation, significant changes occur in the mechanical structure of the tissues of the fetus. The pulp usually softens, becomes more juicy; the bark thins, becomes denser, and in some varieties of pumpkins it even hardens.
A characteristic sign of the ripening of the fruit of all melons is some lightening of their color, but, in addition to this, different species and even varieties of melons have their own special signs of ripening.
When the fruits of watermelons ripen, the tendril located opposite them dries out, the pattern of the bark becomes more noticeable, the sound when clicked is deaf; when squeezing the fetus, a crack appears.
When melons ripen, the color of the bark changes: the pattern becomes clearer, in some varieties the bark is covered with a network of small cracks, and an aroma appears. In many early and mid-season varieties, a sign of ripening is the ease of separation of the fruit from the stalk.
Watermelons, melons and gourds intended for local use are harvested fully ripe; the fruits of watermelons or melons, intended for long-distance transportation, are removed at the very beginning of ripening. The fruits of winter varieties of melons intended for winter storage are also harvested without waiting for full ripening, and when harvesting the fruits, a stalk 3–4 cm long is left.
Fruit picking is a very laborious work, but it can be facilitated by the use of various types of trailed or mounted transport carts, and at the level of watermelons and pumpkins, a square is used, knocked down from round rails at an angle of 85 °. With the help of a tractor-drawn square, the fruits are separated from the lashes and shifted on both sides of the tractor into two solid shafts. The productivity of a square for a 7 hour working day is 16 - 20 hectares. After harvesting, the fruits are sorted. Mature and healthy fruits are sold for consumption or used for storage, ripe but damaged fruits are processed. Small, underdeveloped fruits of watermelons and melons are salted or used for livestock feed.
Melon and watermelon are melon crops, especially demanding on air and soil temperature. They have a longer growing season than the main crops cultivated in Russia. That is why they are grown mainly in the southern regions of the country. However, a high yield of heat-loving gourds can be grown not only in the southern, but also in the central regions of Russia, by planting seeds of early ripening cold-resistant varieties or using seedling planting, as well as protecting plants from spring frosts. In addition, being annual plants, melons and gourds will not bring additional trouble to gardeners, vegetable growers, such as apricots or grapes. Despite this, in Russian garden plots it is not often possible to find beds on which honey melon or sweet juicy watermelon grow. Growing melon and watermelon, of course, requires some effort, but even not very experienced vegetable growers can create the right conditions for their growth. The secret of success is the choice of a suitable crop variety and the right agricultural technology.

The secret of success in growing watermelons and melons is the choice of a suitable crop variety and the right agricultural technology.
Choice of melon and watermelon varieties

Before planting, the seeds are soaked - in a container with boiled water, it is necessary to knead a leaf of aloe (the volume of water should be about 5 times the volume of the leaf), lower the seeds for 6 hours.
For cultivation in the central regions of Russia, only early ripening cold-resistant varieties of melons and watermelons are suitable. When choosing seeds, it is necessary to pay attention to the duration of the growing season, that is, the number of days from the beginning of growth to the ripening of the crop. Watermelons and melons of early varieties should have time to grow and ripen in a period not exceeding 90 days.
The climate features of the central regions of the country will not allow growing a large fruit. It is best to give preference to medium-sized varieties, which in terms of their taste are in no way inferior to the southern "giants".
To get a high yield, the best varieties of watermelons are: Pink Champagne, Spark, Siberian Lights, Moscow Region Charleston, Siberian Rose, Krimstar, Gift to the North and others. Of the melon varieties of interest are: Cinderella, Dessertnaya 5, Dubovka, Thirty Days, Iroquois, Golden, Northern Cantaloupe, Kharkiv early and others.
Agrotechnics and care for early ripening cold-resistant varieties of melons and watermelons are not much different from the rules for growing, for example, carrots, beets or cabbage.
All these crops in the center of Russia are grown by direct sowing of seeds in open ground in mid-late May. Melon crops of other varieties can be grown only in a greenhouse way or through seedlings, while reducing the time spent on open ground. These varieties include mid-season varieties of popular Astrakhan watermelons or melons: Kolkhoznitsa, Pineapple and Medovaya.
Back to index
Sowing seeds of melons and watermelons
By direct sowing in open ground of seeds in the territory of the central regions of Russia, only early-ripening varieties of melons and watermelons are grown, as already noted. For sowing, it is recommended to use 2-year-old or 3-year-old seeds, which, as practice has shown, bloom earlier than accelerate the process of fruit ripening. In cases where sowing will be carried out with fresh seeds, they must first be dried for 2-3 days at a temperature of 30-35ºС.

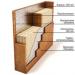
Types of insulated soil: 1 - steam pit; 2 - steam combs; 3 - steam ridge.
It is better to plant seeds in a nested way, placing holes, depending on the variety, at certain distances. So, short climbing varieties can be planted thicker, and long climbing varieties less often. The optimal distance between the holes is at least 1 m.
Prior to sowing seeds, it is necessary to add 1-1.5 kg of humus or compost to each well. In addition, the application of phosphorus and potassium mineral fertilizers can be recommended for watermelons.
The seeds of melons and watermelons are planted to a depth of about 5 cm, after which the soil is generously watered with warm water. Seeds germinate after sowing in about 8-10 days.
Watering the growing shoots should be carried out with warm water as the soil dries abundantly, but not often, but about once a week.
As experts emphasize, when forming a plant, the process of pinching the tops of the shoots is important. This process is necessary, since female flowers begin to develop better on second-order shoots. Pinching should be done when 5-6 leaves appear on the shoot of a melon or watermelon. It is possible to carry out repeated minting of plants, when 5-6 leaves appear on the shoots of the second order.
Back to index
Growing seedlings of gourds
The seedling method of growing melons and gourds allows you to get a good harvest of melons and watermelons with a growing season of more than 90 days. Seedlings of gourds should be grown in pots to avoid damage to the root system during planting.
You can grow melon and watermelon seedlings ready for planting in about 30 days. Before sowing seeds in pots, they can be soaked and germinated, which will reduce the period of emergence of seedlings.

The first female flower of a watermelon appears on the main stem: in early varieties after the 5-6th node and in later varieties after the 12-14th node.
Care for seedlings of melons and watermelons has features. First of all, it is necessary to provide an air temperature of at least 20ºС to obtain good seedlings. On cloudy days and at night, it is best to lower the temperature a little to prevent the plants from stretching. In addition, it is necessary to control that the plants do not touch the leaves, and periodically push the pots apart.
There is no need for additional lighting of seedlings, since the seeds of gourds for seedlings are sown around the middle or end of April, when there is enough natural light. But plant nutrition is necessary. It is best to do 2 fertilizing during the growing period.
Ready seedlings should have 3 to 5 leaves. Melon seedlings have their own characteristics: the formation of female flowers on the lateral shoots occurs earlier than on the main shoot. That is why the tops of plants ready for planting must be pinched. About a week before the date when the seedlings are planned to be planted, the daytime temperature is reduced to 15ºС, and the night temperature is reduced to 12ºС. In addition, periodic airing of plants is carried out. Thus, the seedlings are hardened and prepared for planting in open ground.
Back to index
Planting seedlings of melons and watermelons

A feature of the melon is the absence of female flowers on the main stem - therefore, the first pinching is carried out over the 3rd leaf.
In order to do without greenhouses and hotbeds, you should not hurry with planting seedlings of melons and watermelons. Very often in the territory of the central regions of Russia, fine weather sets in at the beginning of May, which worsens noticeably by the middle of the month. Sometimes frosts occur during this period. Under such conditions, seedlings of melons and gourds may die. That is why it is best to plant seedlings at the end of May, having previously read the weather forecast.
In cases of unexpected cold snap, the shoots of melons and watermelons will require additional care: a temporary film shelter - a greenhouse will need to be built over the plants.
Seedlings are planted in holes, as noted, at a distance of at least 1 m. Two plants can be planted in one hole, provided that in the future the growing shoots will be directed in opposite directions.
Planting melons and watermelons in a small area requires the preliminary application of at least 2 kg of humus or compost to each well. This is best done a week or two before transplanting. Immediately before planting, the wells are abundantly watered with warm water, the plants are carefully removed from the pots and planted in the slurry formed from watering. In order to avoid rotting of plants, deepening of seedlings is not allowed: the seedling clod should protrude above the soil surface.
The most delicious is the watermelon that grew in the garden and was nourished by the sun, greenhouse fruits do not have such a taste. That is why gardeners tend to grow watermelons in the open field, but not everyone succeeds.
Planting watermelon seeds in open ground
There are many issues associated with growing watermelons, but the most important of them is seed preparation and planting methods.
Watermelon seeds do not germinate well, as they are covered with a dense shell. Without pre-treatment of seeds, seedlings may not appear. First of all, experienced gardeners calibrate the seeds, for this they are dipped in a strong saline solution. All heavy seeds will sink to the bottom of the container, and they are used for further cultivation. Light seeds are unsuitable for planting.
Shortly before planting, the seeds are processed and disinfected, placed in a hot solution, then placed in a cold environment. The water temperature should not exceed 55°C. The solution is prepared from potassium permanganate, then the seeds are washed in clean water.
Planting watermelon seeds in a seedless way
After processing, the seeds are planted on the beds, this is done only in regions with a mild climate. Best of all, the seeds germinate at a soil temperature of 12-15 ° C, so they start planting in early spring.
The depth of seed placement depends entirely on soil structure and seed size. On light and loose soils, it ranges from 4 to 8 cm, on heavy soils - no more than 6 cm. Moreover, small seeds are sown in shallow grooves or holes, while larger ones are planted deeper.
Landing is carried out according to one of the schemes:
Ordinary method. Between the bushes leave from 70 to 150 cm, between rows of at least 1.5 m.
Square nest. Bushes are planted at a distance of 70 to 210 cm.
For normal growth and development, the fruits need a lot of sun, plantings should not be thickened. In addition, it will protect plants from possible diseases and pests.
Another advantage of such a sparse landing is the abundance of food. The fact is that each fruit must receive enough nutrients. With thickened plantings, nutritional deficiencies occur.
Growing watermelons through seedlings
If the spring is long and cold, then it is better to plant prepared seedlings in the open ground after the heat is established. The whole process takes from 20 to 35 days, it all depends on the variety chosen.

For cultivation, a loose nutrient mixture is prepared, which consists of peat, humus and soddy soil. The depth of planting in cups is only 3-4 cm. Watermelon seeds are large, so they are immediately planted in separate containers so as not to injure the taproot with frequent transplants.
After planting, the containers are placed in a greenhouse until shoots appear. During this period, the temperature in the room is maintained at the level of 20-25°C, at night it is allowed to drop to 18°C. After the appearance of sprouts, the containers are removed to a colder place for 4 days to prevent stretching. The temperature is maintained at the same level - 17-18°C, further the seedlings are grown at a temperature of 20°C.
When caring for seedlings, special attention is paid to watering. They should not be plentiful, but you do not need to keep the sprouts dry. Water the plants only with warm water, trying not to get on the tender leaves.
The first feeding is carried out a week after the emergence of shoots. Use complex mineral mixtures for seedlings or melons.
Shortly before the intended planting in the ground, the plants are hardened. To do this, they are briefly taken out into the street, gradually increasing the residence time. Seedlings are planted from mid-May to early June.
How to choose a site for growing watermelons in open ground
A place for growing is chosen taking into account all the features of melons.
The site should be well lit throughout the day, be protected from cold winds and drafts.
Watermelons grow best in light soil, so take care of its condition in advance.
Since autumn, the beds are enriched with organic matter, humus or manure is introduced. In the spring, the place is dug up, weeds are removed.
Mineral fertilizers are applied under plowing:
Ammonium sulfate - 25 gr;
Superphosphate - 40 gr;
Potassium - 15 gr.
Plants are planted on prepared beds according to any of the above schemes. At first, the bushes shade from the scorching sun.

Features of growing and caring for watermelons in the open field
Watermelons are relatively undemanding crops, but without minimal care, you will not be able to get a good harvest of fruits. First of all, plants need watering, which carry out in a specific pattern:
Before the appearance of flowers, water sparingly;
Abundant during fruit set;
During the ripening period, reduce to a minimum and completely stop.
This technology allows you to grow juicy fruits with sugar pulp.
The frequency of watering also depends on the soil on which the crop is grown. On sandy soil, it is watered more often, and on chernozem and clay soils, it is somewhat less common.
Another important point when growing watermelons in open ground is top dressing. Feed three times per season:
10 days after planting seedlings or germination;
During the flowering period;
During the formation of ovaries.
Mineral fertilizers with a low nitrogen content are used for top dressing, which reduces the risk of nitrate accumulation in fruits.
In addition, the main care for watermelons consists of the following procedures:
Loosening the soil to a depth of 7 cm;
Weed removal;
Whip protection from winds;
Pest and disease control.
After each watering or rain, the soil is carefully loosened, weeds are removed until the lashes between the bushes occupy all the free space. To protect the whips from the wind, they are pinned to the ground and sprinkled.
Problems when growing watermelons in open ground
If the site gets wet from moisture or there is not enough light and space for growing, then vertical supports can be installed. They must be strong to withstand the load of the growing fetus. Only one main lash is left on the plant, on which up to 3-4 fruits are allowed.
If frosts are expected, then plantings should be covered with cardboard or covering material.
Wet weather can encourage aphids and fungal diseases. Regularly inspect the bushes, if necessary, carry out preventive spraying with a solution of garlic, tobacco dust or ash. In case of mass destruction, chemical preparations are used.
When to pick watermelons
How to determine the ripeness of a crop so as not to collect an unripe fruit? Experienced gardeners rely on the timing of planting and the duration of the growing season, for example, early varieties produce a crop in mid-August. Mass crops are not harvested, but only ripe fruits are selected. They can be distinguished by their characteristic features:
The crust is shiny, smooth and dense;
When tapping, a dull sound;
Dry stalk and bract.
If the berry is planned to be transported to the place of storage, then it is better to collect the unripe one. They mature in storage.